How To Register Taxonomy For Custom Post Type
Better import and export handling, advanced queries with tax_query, hierarchical support, trunk classes and a bunch of wonderful functions to play with were all part of the package.
Allow's take an in-depth look at how to create your own custom taxonomies in WordPress, including a few advanced development examples that you can brainstorm using in your WordPress themes and plugins today.
Farther Reading on SmashingMag:
- Customizing WordPress Archives For Categories, Tags And Other
- Building An Avant-garde WordPress Search With WP_Query
- Introducing Term Meta Data In WordPress And How To Use Them
- The Complete Guide To Custom Mail Types
The Custom Taxonomy In WordPress
WordPress' custom taxonomies brand it possible to structure large amounts of content in a logical, well-organized way. In WordPress, categories are set up as a hierarchal taxonomy, and tags are set equally a multifaceted taxonomy.
More after jump! Continue reading below ↓
Taxonomy content tin can exist displayed in a theme using taxonomy templates. Within a template, at that place are ample means to display your data with born taxonomy functions.

Built-In Taxonomies
WordPress offers four born taxonomies out of the box:
- Categories (hierarchal),
- Tags (multifaceted),
- Links (multifaceted),
- Navigation carte du jour (hierarchal).
Custom Taxonomies
WordPress provides a new method of grouping content by allowing you to create your own custom taxonomies. The core developers have created the register_taxonomy() function to handle the heavy lifting for u.s.. All you have to do is understand how to configure all of the settings to suit your needs.
A Practical Example: Content Past Location
A business that operates in multiple locations could benefit from organizing its content by location to allow visitors to browse news in their locality. A big news organization could organize its content past world region (Africa, Asia, Europe, Latin America, Centre East, US & Canada), equally the BBC does in its "World" section.

Create a Custom Taxonomy
In WordPress, you tin create (or "register") a new taxonomy by using the register_taxonomy() part. Each taxonomy choice is documented in detail in the WordPress Codex.
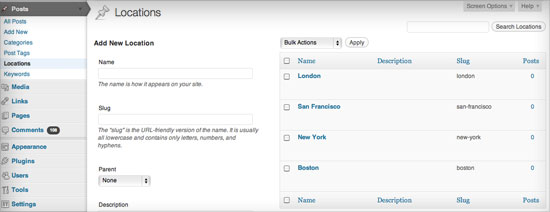
/** * Add custom taxonomies * * Additional custom taxonomies can be divers here * https://codex.wordpress.org/Function_Reference/register_taxonomy */ function add_custom_taxonomies() { // Add together new "Locations" taxonomy to Posts register_taxonomy('location', 'post', array( // Hierarchical taxonomy (like categories) 'hierarchical' => true, // This assortment of options controls the labels displayed in the WordPress Admin UI 'labels' => array( 'name' => _x( 'Locations', 'taxonomy general proper noun' ), 'singular_name' => _x( 'Location', 'taxonomy singular proper name' ), 'search_items' => __( 'Search Locations' ), 'all_items' => __( 'All Locations' ), 'parent_item' => __( 'Parent Location' ), 'parent_item_colon' => __( 'Parent Location:' ), 'edit_item' => __( 'Edit Location' ), 'update_item' => __( 'Update Location' ), 'add_new_item' => __( 'Add New Location' ), 'new_item_name' => __( 'New Location Proper noun' ), 'menu_name' => __( 'Locations' ), ), // Control the slugs used for this taxonomy 'rewrite' => array( 'slug' => 'locations', // This controls the base of operations slug that will brandish before each term 'with_front' => imitation, // Don't display the category base before "/locations/" 'hierarchical' => true // This volition permit URL's similar "/locations/boston/cambridge/" ), )); } add_action( 'init', 'add_custom_taxonomies', 0 ); After adding this to your theme'due south functions.php file, yous should see a new taxonomy under the "Posts" menu in the admin sidebar. Information technology works just like categories just is separate and contained.

After adding a few terms to your new taxonomy, you can begin to organize the content in your posts by location. A new "Locations" box volition appear to the right of your posts in the WordPress admin area. Use this the way you would categories.
Allow's apply this "location" taxonomy every bit a jumping-off point to learn more about working with taxonomy functions and content.
Create a Taxonomy Template for Your Theme
When you add together a custom taxonomy to a WordPress theme, you can display its content using i of WordPress' taxonomy theme templates.
-
taxonomy-{taxonomy}-{slug}.phpWe could utilise this to create a theme template for a detail location, such every bittaxonomy-location-boston.phpfor the term "boston." -
taxonomy-{taxonomy}.phpIf the taxonomy werelocation, WordPress would expect fortaxonomy-location.php. -
taxonomy.phpThis template is used for all custom taxonomies. -
archive.phpIf no taxonomy-specific template is found, and then the taxonomy that lists pages will use the archive template. -
index.phpIf no other template is found, then this will be used.
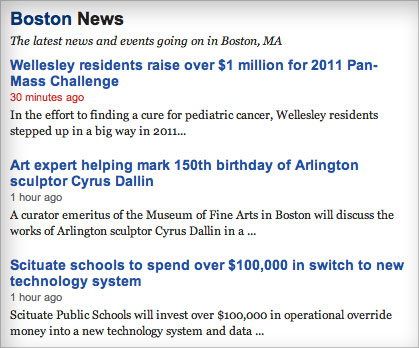
Permit's employ taxonomy-location.php to display our content. The template file could look something like this:
<?php /** * Locations taxonomy archive */ get_header(); $term = get_term_by( 'slug', get_query_var( 'term' ), get_query_var( 'taxonomy' ) ); ?> <div course="wrapper"> <div class="primary-content"> <h1 class="annal-title"><?php repeat apply_filters( 'the_title', $term->name ); ?> News</h1> <?php if ( !empty( $term->clarification ) ): ?> <div class="archive-description"> <?php repeat esc_html($term->description); ?> </div> <?php endif; ?> <?php if ( have_posts() ): while ( have_posts() ): the_post(); ?> <div id="post-<?php the_ID(); ?>" <?php post_class('post clearfix'); ?>> <h2 class="mail service-championship"><a href="<?php the_permalink(); ?>" rel="bookmark"><?php the_title(); ?></a></h2> <div class="content clearfix"> <div class="postal service-info"> <p><?php the_time(get_option('date_format')); ?> past <?php the_author_posts_link(); ?></p> </div><!--// cease .postal service-info --> <div class="entry"> <?php the_content( __('Full story…') ); ?> </div> </div> </div><!--// terminate #mail service-20 --> <?php endwhile; ?> <div class="navigation clearfix"> <div grade="alignleft"><?php next_posts_link('« Previous Entries') ?></div> <div grade="alignright"><?php previous_posts_link('Next Entries »') ?></div> </div> <?php else: ?> <h2 class="postal service-title">No News in <?php repeat apply_filters( 'the_title', $term->name ); ?></h2> <div form="content clearfix"> <div form="entry"> <p>Information technology seems there isn't anything happening in <strong><?php echo apply_filters( 'the_title', $term->name ); ?></strong> correct now. Check dorsum later, something is bound to happen before long.</p> </div> </div> <?php endif; ?> </div><!--// end .primary-content --> <div form="secondary-content"> <?php get_sidebar(); ?> </div><!--// end .secondary-content --> <?php get_footer(); ?> (Normally, we would load a template function for the loop, but for the sake of simplicity, I've skipped that step. As an alternative to get_term_by(), we could utilize single_term_title() and term_description() on this taxonomy archive template to display or retrieve the title and clarification of the taxonomy term.)
In this example, we've used a part called get_term_by() to call back all of the data associated with a taxonomy term in the grade of an object. The object returned past the get_term_by() function contains the following details about the term:
-
ID325 -
nameBoston -
slugboston -
group0 -
taxonomylocation -
taxonomy ID325 -
descriptionIf you need to know the latest news in Boston, then look no further. -
parent0 (or the ID) -
countone (i.e. the number of posts with this term selected)
Nosotros've used this object, then, to display information about the current term proper name and clarification in the taxonomy-location.php template.
Using Taxonomy Conditionals
Conditional tags tin can be used in WordPress to determine what content is displayed on a item page depending on the conditions met by the page. Taxonomy templates have their ain gear up of conditionals:
-
is_tax()When whatever taxonomy annal page is beingness displayed. -
is_tax( 'location' )When a taxonomy archive page for the "location" taxonomy is being displayed. -
is_tax( 'location', 'boston')When the archive page for the "location" taxonomy with the slug of "boston" is beingness displayed. -
is_tax( 'location', array( 'boston', 'new-york', 'philadelphia' ) )Returnstruewhen the "location" taxonomy annal being displayed has a slug of either "boston," "new-york" or "philadelphia." -
taxonomy_exists()When a particular taxonomy is registered viaregister_taxonomy().
Working With Taxonomy Functions
Many functions for working with taxonomies are available in WordPress. Allow's go through a few commons examples of how to employ them in practise.
Display a List of Taxonomy Terms
Most navigation systems begin with an unordered listing. You can generate an unordered listing of links to taxonomy annal pages using the wp_list_categories() function. This part is very customizable and tin can handle near of the scenarios that y'all'll encounter every bit a theme programmer.
/** * Create an unordered listing of links to active location archives */ $locations_list = wp_list_categories( array( 'taxonomy' => 'location', 'orderby' => 'name', 'show_count' => 0, 'pad_counts' => 0, 'hierarchical' => 1, 'echo' => 0, 'title_li' => 'Locations' ) ); // Make certain there are terms with articles if ( $locations_list ) echo '<ul class="locations-list">' . $locations_list . '</ul>'; If you lot encounter a situation that requires a custom construction, I would recommend exploring the Walker class or the wp_get_object_terms() role.
Create a Taxonomy Tag Cloud
A tag cloud provides a bully way for users to browse content. The wp_tag_cloud() function makes creating a tag cloud with a custom taxonomy like shooting fish in a barrel.

Let's use it to display a tag cloud of our location terms:
// Locations tag cloud <?php $locations_cloud = wp_tag_cloud( array( 'taxonomy' => 'location', 'echo' => 0 ) ); // Make sure at that place are terms with manufactures if ( $locations_cloud ): ?> <h2>News by Location</h2> <div grade="locations-cloud"> <?php echo $locations_cloud; ?> </div> <?php endif; ?> Become All Terms in a Taxonomy
You will oft need to piece of work with a full list of terms in a taxonomy, and the get_terms() function can exist quite handy for this. Let'southward use it to bear witness off the number of locations to which we're providing news:
<?php // Get a list of all terms in a taxonomy $terms = get_terms( "location", array( 'hide_empty' => 0, ) ); $locations = array(); if ( count($terms) > 0 ): foreach ( $terms every bit $term ) $locations[] = $term->proper name; $locations_str = implode(', ', $locations); ?> <h2>Nationwide Coverage</h2> <p>Nosotros cover stories effectually the country in places similar <?php echo $locations_str; ?> and more than. If we're not the best source for the latest news in your surface area, permit the states know!</p> <?php endif; ?> This will output the following HTML:
<h2>Nationwide Coverage</h2> <p>We encompass stories around the land in places similar Boston, London, New York, San Francisco and more. If we're not the best source for the latest news in your expanse, let us know!</p> This elementary arroyo may non prove information technology, just the get_terms() role is incredibly powerful. It allows you lot to get terms from multiple taxonomies at once by passing an array that contains the names of your taxonomies as the first parameter.
Working With WP_Query and tax_query
The WP_Query form enables you to create a custom loop. WordPress 3.1 introduced a new parameter for the class called tax_query, which allows you lot to brandish content from a taxonomy in many unique means.
Permit'due south use it to create a list of the about recent news posts in Boston.
<?php /** * Display a list of the nearly recent news in Boston * * @class WP_Query https://codex.wordpress.org/Class_Reference/WP_Query */ $locations_query = new WP_Query( array( 'post_type' => 'mail service', 'posts_per_page' => 10, 'tax_query' => array( assortment( 'taxonomy' => 'location', 'field' => 'slug', 'terms' => 'boston' ) ) ) ); // Display the custom loop if ( $locations_query->have_posts() ): ?> <h2>Latest News in Boston</h2> <ul grade="postlist"> <?php while ( $locations_query->have_posts() ) : $locations_query->the_post(); ?> <li><bridge course="date"><?php the_time(get_option('date_format')); ?></bridge> – <a href="<?php the_permalink(); ?>" rel="bookmark"><?php the_title(); ?></a></li> <?php endwhile; wp_reset_postdata(); ?> </ul><!--// end .postlist --> <?php endif; ?> Nosotros could easily brand this set-up dynamic by using the get_term_by() or get_terms() functions that we discussed before.
Attaching Additional Data to a Taxonomy
Each taxonomy term has specific data associated with information technology. Out of the box, WordPress allows you to shop the following information for each taxonomy term:
- Name,
- Slug,
- Parent,
- Description.
Only what if y'all demand to store more than information, such equally an image for the taxonomy term or a championship and description for search engines, or maybe fifty-fifty adhere the term to a detail author the way a traditional news column does? Since WordPress 2.9, developers have been able to adhere boosted meta data to posts, pages, custom post types, comments and users using the add_metadata(), update_metadata() and get_metadata() functions. But this does non include taxonomies such as tags and categories.
With the help of the Taxonomy Metadata plugin, we tin can attach meta data to taxonomy terms for both congenital-in and custom taxonomies. This enables u.s.a. to create additional taxonomy fields that will be stored in a new taxonomymeta database table.
Note to Multisite developers: I've encountered problems using the Taxonomy Metadata plugin on a WordPress Multisite installation. Activating the plugin network-wide results in data not being saved. Instead, actuate the plugin individually for each website, and information technology will work properly.
(Knowing the story behind this technique and what it might mean for future WordPress upgrades is important. Currently, there is a debate on the WordPress Trac projection about the all-time method for this. The method I'll show you lot is one suggested by various WordPress core developers. Just I strongly urge y'all to review the Trac projection and the Codex. A standard approach could very well be built into WordPress in the time to come, which would therefore be more applied than what I am almost to bear witness you.)
The prerequisite to all of the examples below is to install and activate the Taxonomy Metadata plugin.
Add Search Engine Title and Description Fields to Categories and Tags
We will use activeness hooks to gracefully adhere boosted fields to our taxonomies without editing WordPress' cadre. If you've fabricated it this far, and so you probably have a working knowledge of WordPress filters and deportment. To learn nigh working with hooks, I highly advise Daniel Pataki's commodity on the subject.

Let'south start by adding a text input and a textarea field to the "Add New" and "Edit" term pages on the WordPress admin screen. We practise this past placing the following functions in our theme or plugin.
The taxonomy_metadata_add() function attaches the fields to the /wp-admin/edit-tags.php?taxonomy=%taxonomy% page. The %taxonomy% particular in the URL above will modify depending on the term y'all are editing.
/** * Add together additional fields to the taxonomy add view * e.m. /wp-admin/edit-tags.php?taxonomy=category */ office taxonomy_metadata_add( $tag ) { // Only allow users with capability to publish content if ( current_user_can( 'publish_posts' ) ): ?> <div form="form-field"> <label for="meta_title"><?php _e('Search Engine Championship'); ?></label> <input proper name="meta_title" id="meta_title" type="text" value="" size="xl" /> <p class="clarification"><?php _e('Title display in search engines is limited to 70 chars'); ?></p> </div> <div course="course-field"> <label for="meta_description"><?php _e('Search Engine Description'); ?></label> <textarea name="meta_description" id="meta_description" rows="5" cols="40"></textarea> <p class="description"><?php _e('The meta description volition be limited to 156 chars by search engines.'); ?></p> </div> <?php endif; } The taxonomy_metadata_edit() role attaches the fields to the /wp-admin/edit-tags.php?action=edit&taxonomy=%taxonomy%&tag_ID=%id%&post_type=%post_type% folio. The %taxonomy%, %id% and %post_type% items in the URL to a higher place will change depending on the term you are editing.
Nosotros'll use the get_metadata function here to display whatever saved data that exists in the form.
/** * Add additional fields to the taxonomy edit view * east.thou. /wp-admin/edit-tags.php?activeness=edit&taxonomy=category&tag_ID=27&post_type=mail service */ function taxonomy_metadata_edit( $tag ) { // Only allow users with capability to publish content if ( current_user_can( 'publish_posts' ) ): ?> <tr form="course-field"> <th scope="row" valign="superlative"> <label for="meta_title"><?php _e('Search Engine Title'); ?></characterization> </thursday> <td> <input name="meta_title" id="meta_title" type="text" value="<?php repeat get_term_meta($tag->term_id, 'meta_title', true); ?>" size="40" /> <p class="description"><?php _e('Title display in search engines is limited to 70 chars'); ?></p> </td> </tr> <tr class="form-field"> <th scope="row" valign="superlative"> <label for="meta_description"><?php _e('Search Engine Description'); ?></label> </th> <td> <textarea proper noun="meta_description" id="meta_description" rows="v" cols="40"><?php echo get_term_meta($tag->term_id, 'meta_description', true); ?></textarea> <p class="clarification"><?php _e('Title display in search engines is limited to 70 chars'); ?></p> </td> </tr> <?php endif; } These 2 functions control the output of the form fields. I've used HTML that follows WordPress' UI patterns and styles guidelines for the admin area.
Saving the form'south data to the taxonomymeta database tabular array Now that we've added the form fields, we'll need to procedure and save the information with the update_term_meta function that is provided by the plugin.
/** * Save taxonomy metadata * * Currently the Taxonomy Metadata plugin is needed to add a few features to the WordPress core * that let us to shop this information into a new database tabular array * * https://wordpress.org/extend/plugins/taxonomy-metadata/ */ role save_taxonomy_metadata( $term_id ) { if ( isset($_POST['meta_title']) ) update_term_meta( $term_id, 'meta_title', esc_attr($_POST['meta_title']) ); if ( isset($_POST['meta_description']) ) update_term_meta( $term_id, 'meta_description', esc_attr($_POST['meta_description']) ); } Add the new taxonomy fields At present that everything is in place, we'll use action hooks to load our new functions in all the right places. By hooking the following function into the admin_init action, nosotros ensure that information technology runs simply on the admin side of WordPress. First, nosotros need to brand sure that the functions added by the Taxonomy Metadata plugin are bachelor. Side by side, we use the get_taxonomies() function to attach the new taxonomy fields to every public taxonomy, including the built-in tags and categories.
/** * Add additional taxonomy fields to all public taxonomies */ part taxonomy_metadata_init() { // Crave the Taxonomy Metadata plugin if( !function_exists('update_term_meta') || !function_exists('get_term_meta') ) return false; // Go a list of all public custom taxonomies $taxonomies = get_taxonomies( array( 'public' => true, '_builtin' => truthful ), 'names', 'and'); // Attach additional fields onto all custom, public taxonomies if ( $taxonomies ) { foreach ( $taxonomies as $taxonomy ) { // Add together fields to "add" and "edit" term pages add_action("{$taxonomy}_add_form_fields", 'taxonomy_metadata_add', 10, 1); add_action("{$taxonomy}_edit_form_fields", 'taxonomy_metadata_edit', ten, ane); // Procedure and save the data add_action("created_{$taxonomy}", 'save_taxonomy_metadata', 10, one); add_action("edited_{$taxonomy}", 'save_taxonomy_metadata', 10, i); } } } add_action('admin_init', 'taxonomy_metadata_init'); That'southward it. Nosotros're washed!
You lot should now meet two additional fields in your tags, categories and public custom taxonomies. Equally mentioned at the commencement of this department, the technique can exist used to handle many unlike scenarios. This basic framework for storing and retrieving data associated with a taxonomy should have you well on your way to mastering the direction of taxonomy content.
In Conclusion
I promise yous better empathize how to organize WordPress content with the help of taxonomies. Whether hierarchal or multifaceted, a well-implemented taxonomy will simplify the mode content is organized and displayed on a website. WordPress has all of the tools you need to create custom taxonomies and to group your content in new and heady means. How y'all apply them is upwardly to you!
Additional Resources
- Custom taxonomy theme templates in WordPress
- "Custom Taxonomies in WordPress 2.8"
- "A Refresher on Custom Taxonomies"
- Official documentation on
register_taxonomy() - "Introducing WordPress 3 Custom Taxonomies"
- "Calculation Meta Data to Taxonomy Terms"
![]() (al)
(al)
How To Register Taxonomy For Custom Post Type,
Source: https://www.smashingmagazine.com/2012/01/create-custom-taxonomies-wordpress/
Posted by: langleynamonsiver.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Register Taxonomy For Custom Post Type"
Post a Comment